Virtual Machine migration means that first the Virtual Machine is temporarily stopped, a snapshot of it is taken, then this snapshot is moved to the other system and then resumed after that on that system. This process is called VM Migration.
A Snapshot is a state of the virtual machine at a particular point in time.
If a Virtual Machine is migrated, that means its memory, storage, and network connectivity are also transferred to the other host.
The need for Virtual Machine Migration
1) Maintenance
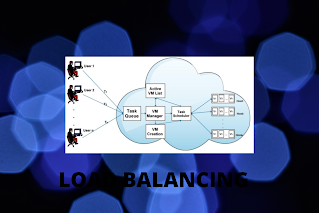
2) Load Balancing
3) In Case of a Host failure, for Recovery purposes.
Types of Virtual Machine Migration
1) Live Migration: In this, RAM pages are getting copied and is marked "dirty", meanwhile the virtual machine is still running.
2) Warm Migration: Suspend the virtual machine for a few seconds, copy the RAM and CPU Registers, then resume on host 2.
3) Cold Migration: Power off the virtual machine on host1, after migrated to host 2 restarts it.
Virtual Machine Memory Migration
1) Pre-copy Memory Migration: In pre-copy memory migration, the hypervisor copies the memory pages to the source system to the destination system. If some of the pages are changed, it is marked dirty and is recopied.
2) Post-copy Memory Migration: In post-copy memory migration, the first virtual machine is suspended, the CPU registers and non-pageable memory is transferred to the destination host.After transfer VM is resumed, even though most of the memory state is in source host.




Helpful
ReplyDeleteRelevant content
ReplyDeleteVery knowledgable..
ReplyDelete